Pneumonia
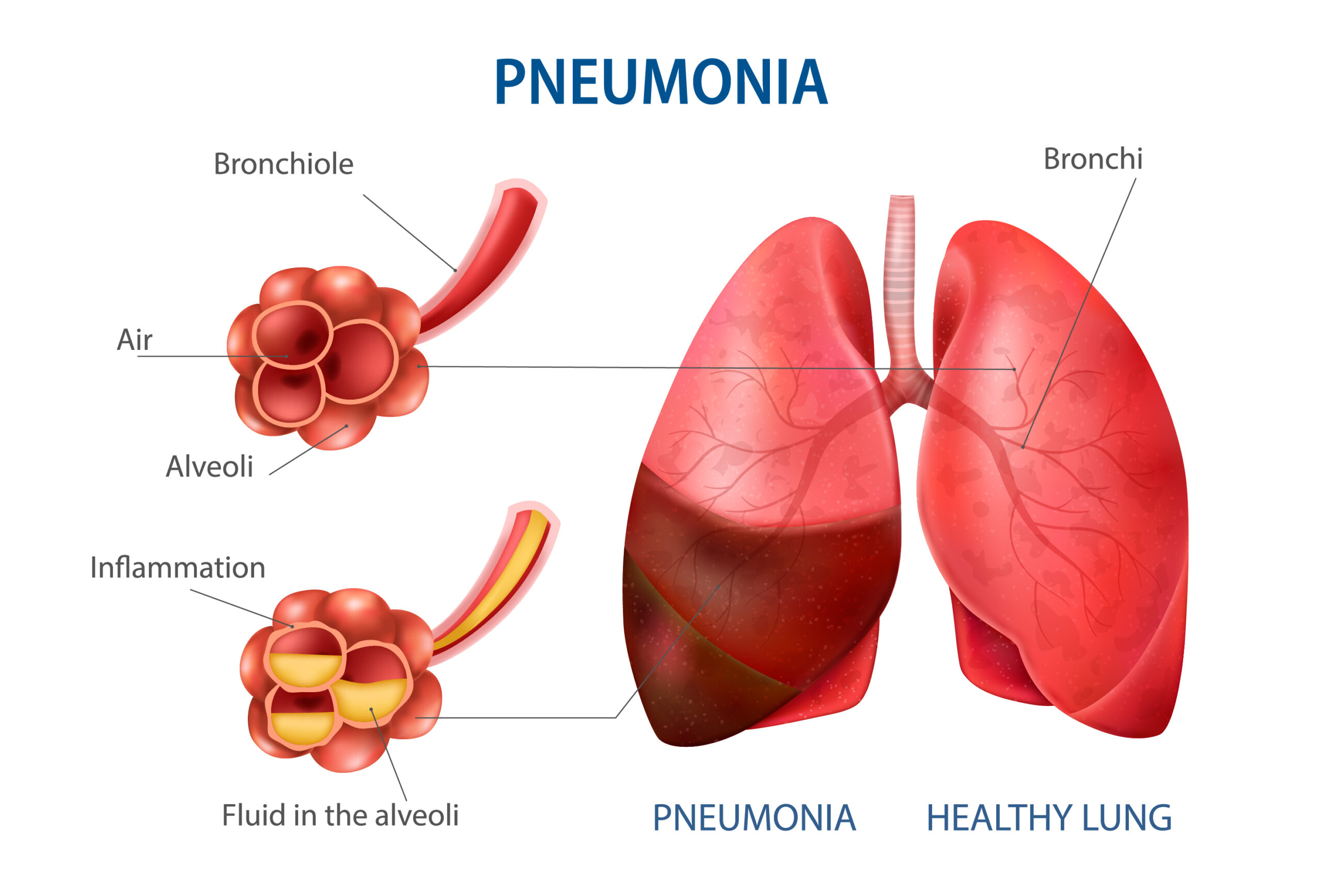
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs typically caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, leading to symptoms such as fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Here’s what you need to know:
- Pneumonia can affect people of all ages but is particularly severe in the elderly, young children, and those with weakened immune systems.
- Common pathogens responsible for pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and respiratory viruses like influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, chest X-rays, and sometimes blood tests to identify the causative agent and determine the severity of the infection.
- Treatment typically includes antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, antiviral medications for viral pneumonia, supportive care to manage symptoms, and oxygen therapy in severe cases.
- Prevention measures such as vaccination against bacterial pathogens like pneumococcus and influenza, practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.